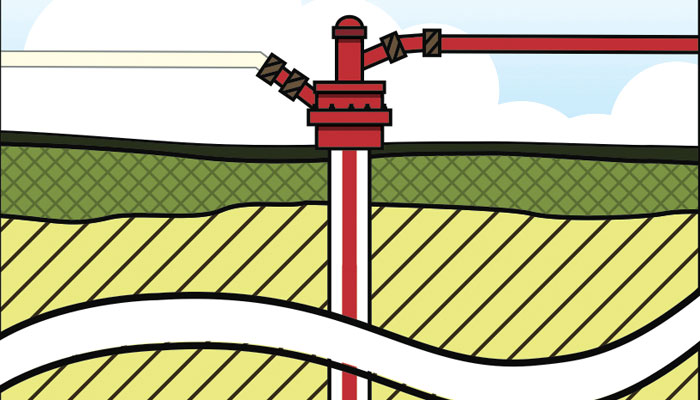
Crestwood Midstream Partners’ proposed 2.1 billion barrel LPG storage facility in the Finger Lakes region of New York State calls for storing propane and butane in large underground caverns created by U.S. Salt during the mining of salt deposits over the last 50 years. Salt caverns are ideal for gas storage because the salt is impermeable, so the gas cannot escape.
This proven technology, which is widely used for propane, natural gas, compressed air and other products, uses brine injection and removal to control propane inflow and outflow from the sealed, pressurized cavern. To receive and store propane, the cavern is completely filled with salty brine. As propane is injected, brine is forced out and stored in adjacent brine ponds or sent to the plant for salt production. To remove propane, the facility operator re-injects brine to force the propane out. Propane is lighter than brine, so the brine inside the cavern resides as a separate layer below.
Storage would be split between propane (1.5 million barrels) and butane (600,000 barrels). Crestwood expects about 80 percent of the product moving through the facility to be moved in and out via pipeline.