All
Data Management: Go Beyond Simple Reporting
by Bryan Walline, ADD Systems
Top 5 Benefits of Business Intelligence Reporting
We are in the Data Age. It’s no longer enough to make business decisions based on intuition; management needs to look at their data for insight. And there is no shortage of data. The key is using the right tools to transform that data into information to help you make the right decisions. That tool is Business Intelligence reporting.
Business Intelligence reporting, often called BI reporting, is software used to collect, analyze, and present data from various sources to help an organization gain insight and actionable information. It is different from the built-in reporting featured in individual software solutions, offering these five key benefits.
1. Actionable insight into your operation
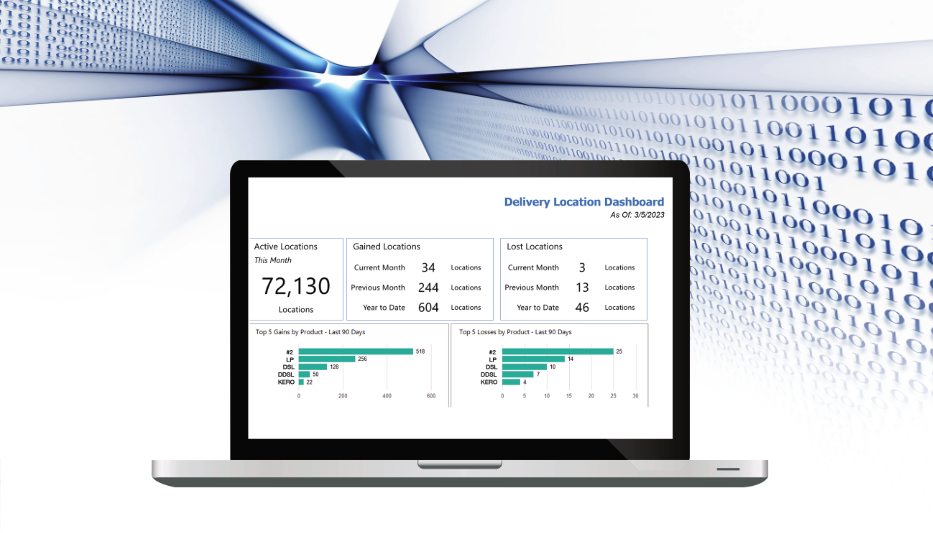
All reports present data, but to make those reports worthwhile, they need to share opportunities for action. With BI reporting, the focus is on, “What can I do with this knowledge?” Through analysis, data is turned into information that is presented with the ability to see snapshots and trends and to drill down to the detail level.
For example, one report might be an account gains and losses view. The goal would be to not only see a snapshot of what is happening, but also to view trends and time period comparisons with drill-down capability for division/product/account detail. The goal is to give insight into any problem, but it also adds another layer of logic: What determines a lost account? No deliveries for the last year? Marked as inactive? BI enables definitions specific to an individual company.
2. Access to all your data
The various systems used to run a business likely have their own reporting, but BI lets you bring them together. For example, payroll system data can be paired with operational data to enable detailed reporting, like delivery history, including driver pay scale information. Without BI, a report like this would require manual compiling, meaning more time and the added possibility of errors.
Another example might be phone system and web portal data. Including these sources with your back-office data enables analysis of phone calls and web portal log ins per customer. This can be a true analysis of web portal adoption and whether it results in fewer calls to the office. It can also show which groups of customers are adopting it well and which are not. Armed with this information, the marketing team can take action.
3. Report Subscriptions and Automatic Alerts
These analytical reports give a window into a business, but there is another key part of a good BI tool: automatic alerts and report subscriptions. The best reports are only helpful if they are used. Report subscriptions simplify that by delivering reports to the necessary viewers on a schedule. If the monthly managers’ meeting occurs the same time every month, the key reports can be automatically created and waiting in the attendees’ inboxes the day before. Without BI, the creation and delivery of those reports could take hours.
Some events also need immediate attention, and those events are customizable. For example, management may want to be notified when there is a COD customer with activity but no payment, or when an automatic delivery customer has a runout. Alerts can be sent to everyone who needs to be informed, so they can react quickly to manage these situations as they arise.
4. Accuracy & Efficiency
Without BI, companies either use reports that come right out of an individual software package or manually manipulate data using tools like Microsoft Excel to create more comprehensive reports. Manual intervention always carries a risk to data integrity. The quality of data is important not only for producing accurate reports, but also for instilling trust in those who rely on the reports. With BI tools retrieving data directly from the source, data integrity is protected.
Efficiency is also a priority for any company, and the design of BI aligns with that goal. BI works with copies of data, whether it be a simple copy of a database or a full data warehouse, optimized for efficient access. The data is updated as frequently as needed, typically once a day outside of business hours. This separation means reporting will not interfere with daily operations.
5. Endless Possibilities
Every business is different. BI is perfect for that. It has the benefits mentioned above, plus endless possibilities. Start out with access to operational data and then add other databases over time, like financial software data, phone system data, client portal data, and more. Management can start out by developing a dashboard of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for their business and a set of standard reports. Then every review of a report will bring new ideas. Your BI software partner can help design new reports tailored to your needs, but IT-savvy companies can also develop their own reports. BI reporting often uses familiar tools like Microsoft, so expertise is easier to come by. Whether you lean heavily on your BI provider or use your own report writers, it will save you time and money to work with people who understand your industry and your data.
There is Much to Gain!
There is actionable information in every company’s data. BI reporting can uncover it efficiently, easily, and proactively, to help a business succeed.
Bryan Walline is Lead Developer – Business Intelligence at energy software company ADD Systems. He can be reached at 800-922-0792 x6025 or wallineb@addsys.com.
Related Posts
 What’s Next in Boiler Technology
What’s Next in Boiler Technology
Posted on June 25, 2025
 Data Delivers!
Data Delivers!
Posted on April 28, 2025
 Harnessing Payment Data to Increase Profitability
Harnessing Payment Data to Increase Profitability
Posted on March 10, 2025
 DeepSeek Is Our AI Wake-Up Call
DeepSeek Is Our AI Wake-Up Call
Posted on March 10, 2025
Enter your email to receive important news and article updates.
